
Power inverter (vehicle power supply) is a kind of convenient power converter that can convert DC12V direct current into AC220V alternating current which is the same as mains power for general electrical appliances. Power inverters come in different capacities, measured in wattage.
Here are 12 key factors to consider when you buy an inverter.
Inverter or Inverter Charger
Both inverters and inverter/chargers provide current from stored battery power, but only inverter/chargers connect to AC sources, pass AC through to equipment, recharge batteries and automatically switch to battery power when AC power is unavailable. Inverters that are not inverter/chargers rely on running vehicles to recharge batteries and do not connect directly to AC sources.
Voltage In
Most commonly, 12V batteries are used to power inverters. This is the type of battery in your car. Heavy-duty inverter/ chargers are also available that use 24V, 36V or 48V batteries for applications requiring higher wattages. Ensure the batteries you choose match the inverter’s input voltage.
Voltage Out
In North America, the electric service coming into your home is 120 volt AC power. If you are in North America, ensure your inverter’s output is compatible with 120V service to power your electronics, power tools or small appliances.
Continuous Output Rating
Determine the total wattage required by all connected devices. The continuous output rating of the inverter or inverter/charger must be greater than the wattage of all the equipment that will be powered simultaneously. You can estimate your wattage needed using Table 2: Typical Wattage of Common Home Appliances.
Input Connection
Small portable inverters plug directly into a vehicle’s 12V receptacle (cigarette lighter). Heavy-duty inverters have DC input terminals that connect directly to batteries with user-supplied cabling. Inverter/chargers connect to both batteries and to an AC power source so that the batteries can recharge when shore power is available.
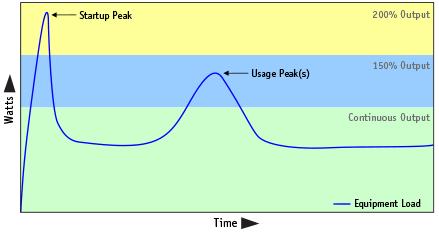
Peak vs. Continuous Power
Many tools, appliances and pumps require brief surges of power when they start up, during use or both. This means temporary wattage is required beyond the continuous power rating of the inverter. Look for an inverter or inverter/charger that can handle such peak power demands by delivering up to 200% of its continuous power rating.
Outlets
Consider how many outlets you will need and whether you need special protection from GFCI outlets for wet or humid environments. Many heavy-duty inverter/chargers can be hardwired into your main electrical panel to provide current directly to your home’s AC outlets. For your safety, use a professional electrician for installation.
Runtime (the amount of time the inverter will provide power for your equipment)
If you’re using an inverter connected to the battery in a running vehicle, you’ll have power as long as the car keeps running. If your inverter or inverter/ charger is running off battery power with no other power source, the runtime depends on the amount of battery power available and the load it is supporting. You can extend your runtime by attaching more batteries. There is no limit to the number of batteries that can be connected.
Cooling Fans
Multi-speed cooling fans prevent heat buildup and prolong your inverter’s service life.
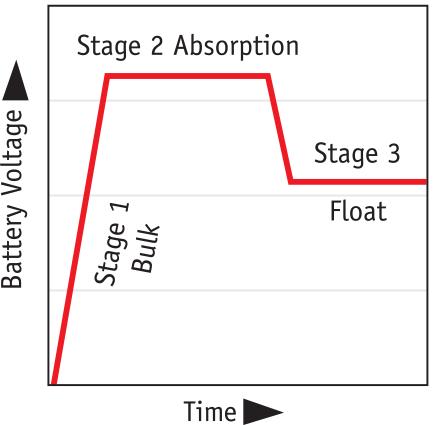
3-Stage Charging
Inverter/Chargers use an advanced 3-stage charger that recharges batteries faster, while protecting them against over-charge, over-discharge and accidental depletion.
Resettable Circuit Breakers
Protect your inverter/charger against damage from overloads or charger failure.
Special Features
When you buy an inverter or inverter/charger, consider if you need any of these special features to power your equipment safely, and how to improve the efficiency of inverter.
- USB ports – Easily charge phones, tablets, wearable fitness trackers and other mobile devices.
- Pure sine wave output – For variable-speed power tools and sensitive electronics like computers, network devices and A/V equipment.
- GFCI outlets – Meet OSHA requirements for use in wet or humid environments, including near sinks.
- Hospital-grade outlets – UL certified for use in patient care areas.
- Remote control capability – Some inverter/chargers provide an RJ45 communication port that enables connection of an optional remote control module.
- Status LEDs – Indicate battery levels and low-battery warnings, load levels, overload warnings, system faults and operation modes.
- Configuration DIP switches – Customize high and low voltage auto transfer to suit your application.
- High initial power – Supports peak surge demands of devices with high initial power requirements, such as motors, compressors and pumps.
